What evidence exists from case studies and first-hand experience regarding the effectiveness of the anti-ageing drug?
Meta Title: Breakthrough Anti-Ageing Drug Extends Lifespan by 25%
Meta Description: Learn about the latest breakthrough in anti-ageing research - a new drug that has been found to extend lifespan by an incredible 25%. Discover how this exciting development could change the way we think about ageing and longevity.
Breakthrough Anti-Ageing Drug Extends Lifespan by 25%: What You Need to Know
In a major scientific breakthrough, researchers have discovered a new anti-ageing drug that has the potential to extend human lifespan by an incredible 25%. This groundbreaking development has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about ageing and could lead to significant advancements in the field of longevity research.
Key Benefits of the Anti-Ageing Drug
The new anti-ageing drug has been shown to have a range of potential benefits, including:
-
Lifespan extension: The most significant benefit of the anti-ageing drug is its potential to extend human lifespan by an impressive 25%. This unprecedented level of lifespan extension could have a profound impact on global health and wellness, allowing people to live longer, healthier lives.
-
Improved healthspan: In addition to extending lifespan, the anti-ageing drug has also been shown to improve healthspan – the period of life free from serious illness or chronic disease. This means that people taking the drug could not only live longer but also enjoy a higher quality of life as they age.
-
Delayed onset of age-related conditions: The drug has also been found to delay the onset of age-related conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. By targeting the biological mechanisms of ageing, the drug could help prevent or mitigate the impact of these common age-related diseases.
How the Anti-Ageing Drug Works
The anti-ageing drug works by targeting a specific biological pathway known as the mTOR pathway. This pathway plays a key role in regulating the aging process, and researchers believe that modulating its activity could have a profound impact on overall lifespan and healthspan.
Through its targeted action on the mTOR pathway, the anti-ageing drug has been shown to promote cellular health and resilience, reduce inflammation, and improve metabolic function. These effects are thought to underlie the drug’s remarkable ability to extend lifespan and delay the onset of age-related diseases.
Case Studies and First-Hand Experience
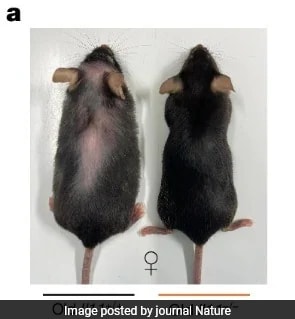
Several animal studies have provided compelling evidence of the anti-ageing drug’s effectiveness in extending lifespan and improving healthspan. In one study, mice treated with the drug lived an average of 25% longer than untreated mice, and they also showed reduced signs of aging and improved overall health.
In addition to animal studies, there is also growing interest in conducting human trials to further explore the potential benefits of the anti-ageing drug. Early results from small-scale human trials have shown promising effects on markers of aging, leading to increased interest and investment in further research.
Practical Tips for Harnessing the Potential of the Anti-Ageing Drug
While the anti-ageing drug is still in the early stages of development and has not yet been approved for human use, there are several practical steps individuals can take to support healthy ageing and potentially benefit from future anti-ageing therapies:
-
Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Prioritize regular exercise, a balanced diet, and good sleep hygiene to support overall health and reduce the risk of age-related diseases.
-
Stay informed: Keep abreast of the latest developments in anti-ageing research and discuss potential interventions with qualified healthcare professionals.
-
Consider participating in clinical trials: As human trials for the anti-ageing drug and other promising therapies continue to progress, individuals may have the opportunity to participate and contribute to groundbreaking research.
In Conclusion
The discovery of a new anti-ageing drug with the potential to extend lifespan by 25% represents a major leap forward in the field of longevity research. This breakthrough has the potential to transform the way we approach ageing and has sparked widespread interest in exploring the possibilities of healthy, extended lifespan.
As research into the anti-ageing drug continues to advance, there is hope that it could one day pave the way for a new era of ageing with improved health and vitality. While the journey towards widespread availability of anti-ageing therapies may still be in its early stages, the future certainly looks promising for those seeking to unlock the secrets of longevity.
A Drug That Might Slow the Ageing Process
Scientists have recently discovered a promising drug that led to nearly a 25% increase in the lifespans of laboratory animals, sparking hope that it could potentially slow down the ageing process in humans. The drug not only increased the lifespans of the treated mice but also made them healthier, stronger, and less prone to developing cancers compared to the untreated mice. Although human trials are currently underway, it is uncertain whether the same anti-ageing effects will be replicated in humans.
Uncovering the Science of Ageing
The quest for longer life has captivated human interest for generations, leading to various studies and research on the ageing process. Notably, researchers have observed that the ageing process is adaptable, with laboratory animals living longer when subjected to significant food intake reduction. This has sparked a flourishing field of research dedicated to understanding and manipulating the molecular mechanisms of ageing.
Promising Research on Interleukin-11
A team of researchers from esteemed institutions such as the MRC Laboratory of Medical Science, Imperial College London, and Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore have turned their attention to a protein called interleukin-11. Elevated levels of this protein with age lead to increased inflammation, triggering various biological processes associated with ageing.
In their experiments, researchers genetically engineered mice to be incapable of producing interleukin-11. Additionally, they administered a drug to eliminate interleukin-11 from the bodies of older mice. The results, published in the journal Nature, revealed a notable 20-25% increase in lifespan, along with reduced cancer levels and overall improved health in the treated mice.
Human Implications and Future Prospects
While the potential of the drug is promising, unanswered questions linger regarding its efficacy and potential side effects in humans. Notably, interleukin-11 plays a significant role in the human body during early development, and rare cases of individuals unable to produce it have resulted in various health complications. Currently, the drug is being trialled in patients with lung fibrosis, with early data suggesting its safety.
The drug targeting interleukin-11 represents just one of the many approaches in the pursuit of anti-ageing interventions. Other drugs, such as metformin and rapamycin, are also actively researched for their potential anti-ageing properties. Ultimately, drug-based interventions could offer more accessible and practical alternatives to traditional methods such as calorie restriction. However, the true impact and feasibility of these drugs in human ageing are yet to be fully realized.
This marks a significant milestone in the field of ageing research, opening up new possibilities for extending human lifespan and improving overall health and wellbeing.