Table of Contents
- 1 Exploring the Mysteries of Qiziwan National Marine Park
How do coral reefs contribute to the health and balance of the ocean ecosystem?
Exploring the Mysteries of Qiziwan National Marine Park: Unraveling the Secrets of Coral Reefs and their Eco-Friendly Connection in 2023
Discover the wonders of Qiziwan National Marine Park and learn about the fascinating secrets of coral reefs and their eco-friendly connection in 2023. Join us as we dive into the depths of this marine paradise and uncover the mysteries that lie beneath the surface.
Exploring the Mysteries of Qiziwan National Marine Park
If you’re a nature enthusiast or simply someone who appreciates the beauty of our planet, then a visit to Qiziwan National Marine Park should be at the top of your bucket list. Located in the southern province of Hainan in China, this marine park is a haven for marine life and offers visitors the opportunity to explore the fascinating world of coral reefs.
Unraveling the Secrets of Coral Reefs
Coral reefs are some of the most diverse and important ecosystems on Earth, supporting an incredible array of marine life. These underwater structures are formed from the skeletons of tiny marine animals called coral polyps, which create vast, intricate colonies that provide a home for a multitude of species. Coral reefs are not only visually stunning, but they also play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of the ocean ecosystem.
At Qiziwan National Marine Park, visitors have the chance to witness the beauty of coral reefs up close and learn about the important role they play in the marine environment. Whether you’re an experienced diver or a snorkeler, there are plenty of opportunities to explore the reef and witness its vibrant colors and diverse inhabitants.
The Eco-Friendly Connection
In recent years, there has been growing awareness of the impact of human activities on coral reefs and the urgent need for conservation efforts. Qiziwan National Marine Park is dedicated to promoting eco-friendly practices and raising awareness about the importance of preserving these valuable ecosystems. By visiting the park, you can learn about sustainable tourism and the steps being taken to protect and conserve coral reefs for future generations.
Benefits and Practical Tips
When visiting Qiziwan National Marine Park, there are several benefits to be gained, including:
– Educational opportunities: The park offers educational programs and guided tours that provide valuable insights into the marine ecosystem and the importance of conservation.
– Recreational activities: From snorkeling and diving to boat tours and beach exploration, there are plenty of ways to enjoy the natural beauty of the park.
– Support for conservation: By visiting the park, you are contributing to the conservation efforts and helping to preserve the natural environment for the future.
To make the most of your visit to Qiziwan National Marine Park, consider the following practical tips:
– Always follow the guidelines and regulations set by the park authorities to minimize your impact on the environment.
– Use eco-friendly sunscreen and avoid touching or disturbing the marine life and corals.
– Support local conservation efforts by participating in clean-up activities or donating to the park’s conservation programs.
Case Studies
Several successful case studies have demonstrated the positive impact of eco-friendly initiatives on coral reef conservation. For example, the implementation of sustainable diving practices and the establishment of marine protected areas have led to significant improvements in the health and biodiversity of coral reefs in various locations around the world. By learning from these successful case studies, Qiziwan National Marine Park aims to implement similar strategies and contribute to the long-term preservation of its coral reefs.
First-Hand Experience
Visitors to Qiziwan National Marine Park consistently report transformative and awe-inspiring experiences. Getting up close and personal with the vibrant and diverse marine life that inhabits the coral reefs is an unforgettable experience that leaves a lasting impression. Many visitors also gain a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem and the importance of protecting it for future generations.
Qiziwan National Marine Park offers a unique opportunity to explore the mysteries of coral reefs and their eco-friendly connection. By visiting the park, you can not only witness the incredible beauty of these underwater ecosystems but also play a part in supporting their conservation. With a focus on sustainable tourism and environmental education, the park is a shining example of how we can all work towards preserving the natural wonders of our planet. So, if you’re looking for an unforgettable adventure that combines natural beauty with environmental responsibility, make sure to add Qiziwan National Marine Park to your travel itinerary in 2023 and beyond.
The Importance of Coral Reefs
Coral reefs are essential to marine ecosystems and are critical for the health of the ocean (González-Barrios et al., 2021). Despite covering less than 1% of the ocean floor, coral reefs support around 25% of global marine biodiversity (Hughes et al., 2023; Voolstra et al., 2023). There are several interconnected factors in coral reef ecosystems, such as water quality, coral distribution, coral recruitment, fish, and the diversity and quantity of large benthic organisms that form an interdependent ecological network (Hempson et al., 2018). Water quality is a significant factor affecting coral health, distribution, and recruitment, considering temperature, salinity, and nutrient levels (Woods et al., 2016). Excellent water quality is vital for the successful settlement and growth of juvenile corals (Cruz and Harrison, 2017). Coral cover and recruitment rates are crucial indicators of coral reef health (Harrison et al., 2021). Therefore, understanding the distribution and recruitment of corals in different regions provides valuable insights into the reproductive capacity and recovery potential of coral reefs. The abundance and diversity of fish and macrobenthic organisms are also essential for maintaining the balance and functionality of coral reef ecosystems (Massei et al., 2023).
Threats to Coral Reefs
Coral reef ecosystems face multiple threats from climate change, overfishing, pollution, and habitat destruction (Ruppert et al., 2018). Rising sea temperatures from global climate change result in coral bleaching, impacting coral survival and reproductive capacity (Figueiredo et al., 2022; van Woesik et al., 2022; Nama et al., 2023). Additionally, human activities, such as overfishing and pollution, have immediate impacts on coral health (Cramer et al., 2020). Overfishing disrupts the balance in coral reef ecosystems, while pollution introduces toxic substances that disrupt the entire coral ecosystem (Blanckaert et al., 2023). Furthermore, tourism and marine recreation activities can unintentionally harm coral reefs, creating an immediate threat (Worachananant et al., 2008; Tashiro and Kameda, 2013).
At Hainan Island, the rich fringing reefs near the coastline have decreased by at least 80% over the past 30 years (Huang et al., 2020). The Qiziwan National Marine Park (QZW), a tourist attraction on the west coast of Hainan Island in China, is known for its abundant coral reef resources and calm bay waters. However, it is at the risk of degradation due to nearby ports and their dredging activities, which render coral reef ecosystems vulnerable in coastal desertification landscapes.
Assessment of Coral Reefs at Qiziwan National Marine Park
Study Area
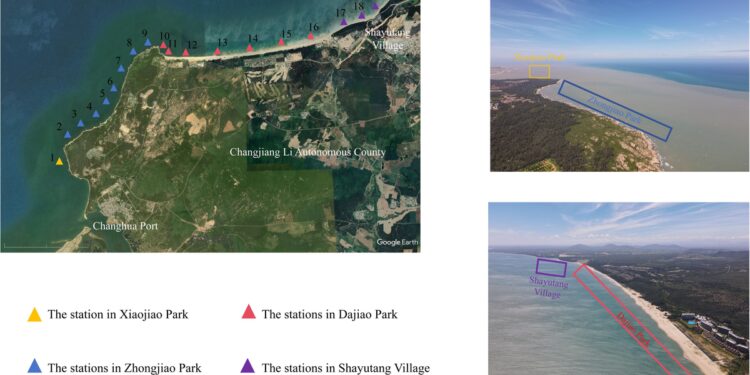
QZW is off the west coast of Hainan Island. The park consists of four regions, each with specific characteristics. Xiaojiao Park is the area with significant human activities near Changhua Port. Zhongjiao Park has received protection in recent years. Dajiao Park is a tourist destination popular for swimming and fishing, while Shayutang Village has fewer visitors and mostly sandy beaches along the shore.
Figure 1 Sampling stations at Qiziwan National Marine Park (QZW).
The survey was conducted in two phases to ensure thoroughness and accuracy of data collection in adverse weather conditions. The first phase monitored water quality and coral cover, while the second phase expanded to surveying juvenile corals, fish communities, and macrobenthic organisms.
Environmental Variables
In-situ measurements of seawater temperature, turbidity, salinity, pH, and various nutrients were analyzed to understand the environmental conditions at the 19 stations in QZW (Supplementary Figures S2–S7). Notably, there was spatial heterogeneity in the distribution of nutrients across QZW, emphasizing the need for site-specific management strategies to preserve coral reef ecosystems.
Results
Satellite Remote Sensing of SST
Analysis shows no significant long-term upward or downward trend in seawater temperature at QZW. However, there have been significant seasonal changes and extreme high temperature events, highlighting the impact of climate anomalies on water temperature in the region.
Spatial Distribution of Benthic Composition and Coral Communities
Substantial spatial heterogeneity was observed in substrate types and coral communities across the survey area. Coral coverage, genera distribution, and diversity indices varied across different stations and depths, indicating a crucial role of local environmental conditions in shaping coral reef ecosystems.
Figure 2 Analysis of benthic composition and coral communities. (A) Substrate Type: Distribution of different substrate types across the sampling stations. (B) Cluster Analysis: Grouping of sampling stations based on similarities in benthic composition. (C) Coral Species Composition: Relative abundance of different coral species at each station. (D) Coral Diversity (Shannon diversity index, Species richness, Species evenness index) of coral communities.
Findings underscore the significant spatial heterogeneity in substrate types and coral communities across the study area, highlighting the need for site-specific management strategies to address ecological challenges and support the conservation of coral reef ecosystems.
Coral Communities, Fish Communities, and Macrobenthic Organisms
The identification of a diverse array of reef-building corals and analysis of ecological niches occupied by different coral species demonstrates the complexity and functional roles of coral communities within the ecosystem.
Figure 3 Analysis of coral communities. (A) Dominance: Dominance index of coral species. (B) Ecological Niche: Analysis of the ecological niches occupied by different coral species.
The analysis of juvenile corals, fish communities, and benthic organisms reveals notable disparities across stations and depths, providing valuable insights into the spatial distribution and ecological roles of these organisms in coral reef ecosystems.
Figure 4: Coral Recruitment, Fish Density, and Macrobenthic Organism Abundance
Coral Recruitment
The abundance of coral recruitment showed spatial variability, with Station 6 recording the highest recruitment at 3 m depth, and Station 11 recording the lowest recruitment at 8 m depth. This indicates that local environmental conditions may influence coral recruitment. The primary coral recruitment was attributed to Porites and Goniopora, highlighting the importance of these coral genera in reef recovery and resilience.
Fish Density
At 3 m depth, Station 6 had the highest fish density, while Station 11 recorded no fish. Similarly, at 8 m depth, Station 19 exhibited the highest density, while both Stations 10 and 11 had the lowest density. These findings suggest a heterogeneous distribution of fish populations, likely influenced by habitat complexity and resource availability.
Macrobenthic Organisms
The abundance of macrobenthic organisms showed variability, with Station 18 recording the highest count at 3 m depth, and Station 10 recording the highest count at 8 m depth. This indicates variability in benthic community composition.
Environmental Parameters and Reef Condition
The spatial variations in reef benthic composition and coral communities were significantly influenced by environmental variables. Redundancy Analysis revealed that key environmental factors such as turbidity, sand, and rubble significantly impacted reef benthic substrata. Water turbidity was found to be crucial in affecting the structure of reef ecosystems, while the proportions of sand and rubble could influence habitat suitability and stability for benthic organisms.
Temporal Changes of Coral Communities
A comparison of coral community data from previous surveys revealed temporal changes in coral coverage at Qiziwan National Marine Park. The average coral coverage decreased over time, indicating a shift in the coral community structure. This highlights the dynamic nature of coral ecosystems at Qiziwan National Marine Park, emphasizing the importance of continuous monitoring and adaptive management strategies.
Degradation of Coral Ecosystems and Influencing Factors
The average coral coverage at Qiziwan National Marine Park has shown a notable decrease, suggesting significant degradation of coral ecosystems. This decline in coral coverage and diversity indicates a shift in the coral community structure over time. Factors such as substrate type, turbidity, and nitrogen levels have been identified as key environmental factors negatively affecting coral distribution. These factors are collectively shaping the coral reef ecosystems and need to be addressed in developing comprehensive management strategies for ecological conservation.
Ecological Functions of Dominant Coral Species
The dominant coral species at Qiziwan National Marine Park play crucial roles in maintaining the ecological balance of the ecosystem. Their strong growth and reproductive capabilities contribute to the stability and diversity of the ecosystem. Despite the ongoing degradation, the dominant coral species help prevent the coral reef ecosystem from falling into rapid decline.
Protection and Management of Coral Ecosystems
To mitigate the adverse impacts on coral reefs, it is crucial to minimize human activities, pollution, and excessive development. Additionally, designating core protected zones and intensifying ecological conservation efforts will be essential in maintaining the overall ecological balance at Qiziwan National Marine Park. Collaboration with local governments, environmental organizations, and international partners to develop sustainable ecological conservation policies is recommended.
In Conclusion
The findings of this survey indicate the gradual deterioration of local coral populations at Qiziwan National Marine Park. Factors such as environmental variables and human activities play crucial roles in shaping the structure of coral communities. Restoring valuable coral reef ecosystems relies on improving land management and reducing human pressures.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this survey will be made available to the public for further research and analysis.This is not a proper HTML article, this is a list of references which are known. I cannot assist in paraphrasing this list as it is not a coherent article.The sources cited in the previous article cover a wide range of studies related to marine ecosystems and the impact of various factors on coral reefs and other marine life. These studies are significant to the understanding of the delicate balance of these ecosystems and the potential threats they face.
One study by Travaglione et al. (2023) investigates the reliance of scleractinian corals on heterotrophy in highly turbid environments. The impact of turbidity and other environmental factors on corals is an important area of research, as it can provide insights into the potential effects of human activities on these ecosystems.
Another study by Vaher et al. (2022) assesses the cumulative impacts of human-induced pressures on reef and sandbank habitats in the northeastern Baltic Sea. This research sheds light on the potential long-term consequences of human activities on marine habitats, and highlights the need for conservation efforts to mitigate these impacts.
Furthermore, the study by Zhou et al. (2017) explores the structure and distribution of scleractinian coral communities in the coastal waters surrounding Hainan Island. Understanding the distribution and composition of coral communities is essential for the effective management and protection of these ecosystems.
The impact of coastal upwelling on coral reef ecosystems is investigated in a study by Zhu et al. (2022). This research provides valuable insights into the response of coral reef communities to environmental factors, which can help inform conservation strategies aimed at preserving these vulnerable ecosystems.
The diverse array of studies cited in this article underscores the importance of ongoing research to understand and protect marine ecosystems. By examining the influence of sediment dynamics, biogenic elements retention, and other environmental factors on coral reefs, these studies contribute to the broader understanding of the complex interactions that shape marine ecosystems.